Mollenol and Adult Molluscum Contagiosum
3rd Jul 2025
 Mollenol is a topical, all-natural product used to manage the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum in both children and adults. It contains ingredients such as clove bud oil and coconut oil, which are traditionally used in Western herbal medicine to relieve minor skin eruptions, mild eczema, skin inflammation, and act as an antimicrobial and counterirritant[1][2]. Mollenol is available in different strengths: a sensitive lotion for use on the face and private parts, and a full-strength lotion for other areas of the body in adults[3][1]. Mollenol patches can also be used, especially for pus-filled bumps, and are suitable for use anywhere on the body except very hairy areas[3].
Mollenol is a topical, all-natural product used to manage the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum in both children and adults. It contains ingredients such as clove bud oil and coconut oil, which are traditionally used in Western herbal medicine to relieve minor skin eruptions, mild eczema, skin inflammation, and act as an antimicrobial and counterirritant[1][2]. Mollenol is available in different strengths: a sensitive lotion for use on the face and private parts, and a full-strength lotion for other areas of the body in adults[3][1]. Mollenol patches can also be used, especially for pus-filled bumps, and are suitable for use anywhere on the body except very hairy areas[3].
Mollenol is not a cure for the viral infection itself but is used to minimize symptoms, provide moisture, and counteract inflammation associated with molluscum contagiosum[4][3]. It is recommended to confirm the diagnosis with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment[4].
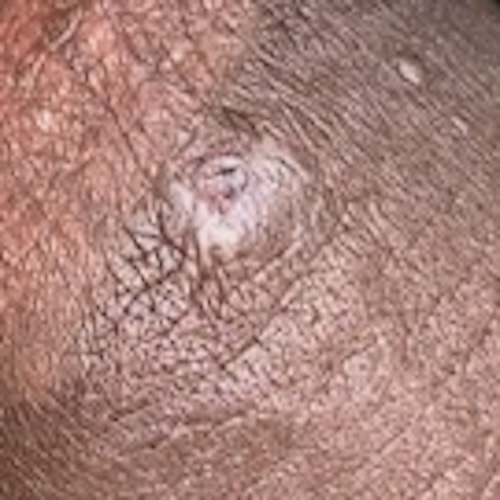
Pictures of Molluscum Contagiosum in Adults
Molluscum contagiosum in adults typically presents as small (1–6 mm), firm, pink, white, or skin-colored bumps with a characteristic central dimple (umbilication)[5][6][7]. Lesions are often clustered and may appear in a straight line due to scratching (self-inoculation). In adults, the most commonly affected areas are the genitals, lower abdomen, buttocks, and inner thighs, especially when acquired through sexual contact[5][8]. In immunocompromised adults, lesions can be larger and more widespread[5].
For visual references, reputable medical sites such as DermNet and eMedicineHealth provide extensive image galleries of molluscum contagiosum in adults[6][9][5].
Duration of Molluscum Contagiosum in Adults
Molluscum contagiosum is a self-limiting infection, but its duration can vary:
- Without treatment: Lesions typically resolve on their own within 6–12 months, but in some cases, they may persist for up to 2 years or even longer[10][11][12][7][13][14].
- With treatment: Medical or topical treatments (including Mollenol) may help reduce symptoms and speed up resolution, but there is no guaranteed way to immediately eradicate the virus[10][12][7].
- In immunocompromised individuals, the infection can last significantly longer and be more severe[15][16][14].
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum in Adults
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a poxvirus (molluscum contagiosum virus)[17][18][19]. In adults, the main routes of transmission are:
- Skin-to-skin contact: Especially during sexual activity, which is the most common route in adults[17][18][1].
- Contact with contaminated objects: Such as towels, clothing, gym equipment, and pool surfaces[17][18][19].
- Self-inoculation: Scratching or shaving over lesions can spread the virus to other areas of the skin[17][19].
Adults with weakened immune systems (e.g., HIV-positive, on immunosuppressive therapy) are at higher risk for more extensive and persistent infections[15][16][8].
Prevalence and How Common Molluscum Contagiosum Is in Adults
- Molluscum contagiosum is much more common in children, but it does occur in adults, especially young sexually active individuals and those with weakened immune systems[16][8][20].
- Studies indicate that about 8% of molluscum cases occur in adults, with a higher prevalence among men (male-to-female ratio of about 3:1 in adults)[16][8][20].
- The overall prevalence in adults is estimated at around 8%, and the infection is more common in men and in those with HIV or other immune deficiencies[16][8][20].
- There is no racial or geographic predilection for the infection[20].
Summary Table: Key Facts About Molluscum Contagiosum in Adults
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Cause |
Poxvirus (molluscum contagiosum virus) |
|
Transmission |
Skin-to-skin (often sexual), contaminated objects, self-inoculation |
|
Appearance |
Small, firm, dome-shaped, umbilicated bumps (1–6 mm), often clustered |
|
Common Locations |
Genitals, lower abdomen, buttocks, inner thighs |
|
Duration |
6–12 months (may last up to 2 years or more) |
|
Prevalence in Adults |
~8% of cases, more common in men and immunocompromised individuals |
|
Complications |
Secondary bacterial infection if lesions are scratched; scarring is rare |
References: [4][6][10][15][17][16][8][3][5][11][12][18][20][1][7][13][19][2][9][14]
If you suspect you have molluscum contagiosum, consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and to discuss the best management approach for your situation.
- https://www.mollenol.com/molluscum-contagiosum-treatment-adults/
- https://www.mollenol.com/molluscum-contagiosum-treatment-mollenol-sensitive-pack/
- https://www.mollenol.com
- https://www.mollenol.com/molluscum-home-treatment/
- https://skinsight.com/skin-conditions/molluscum-contagiosum/
- https://dermnetnz.org/images/molluscum-contagiosum-images
- https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/skin-infection/molluscum-contagiosum-pictures-causes-treatment
- https://escholarship.org/uc/item/308500hv
- https://www.emedicinehealth.com/image-gallery/molluscum_contagiosum_picture/images.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12175-molluscum-contagiosum
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/molluscum-contagiosum
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/molluscum-contagiosum
- https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/healthwise/molluscum-contagiosum
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/molluscum-contagiosum
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/910570-overview
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10453394/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/molluscum-contagiosum/symptoms-causes/syc-20375226
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/molluscum-contagiosum-causes
- https://www.cdc.gov/molluscum-contagiosum/about/index.html
- https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Molluscum_contagiosum_epidemiology_and_demographics
